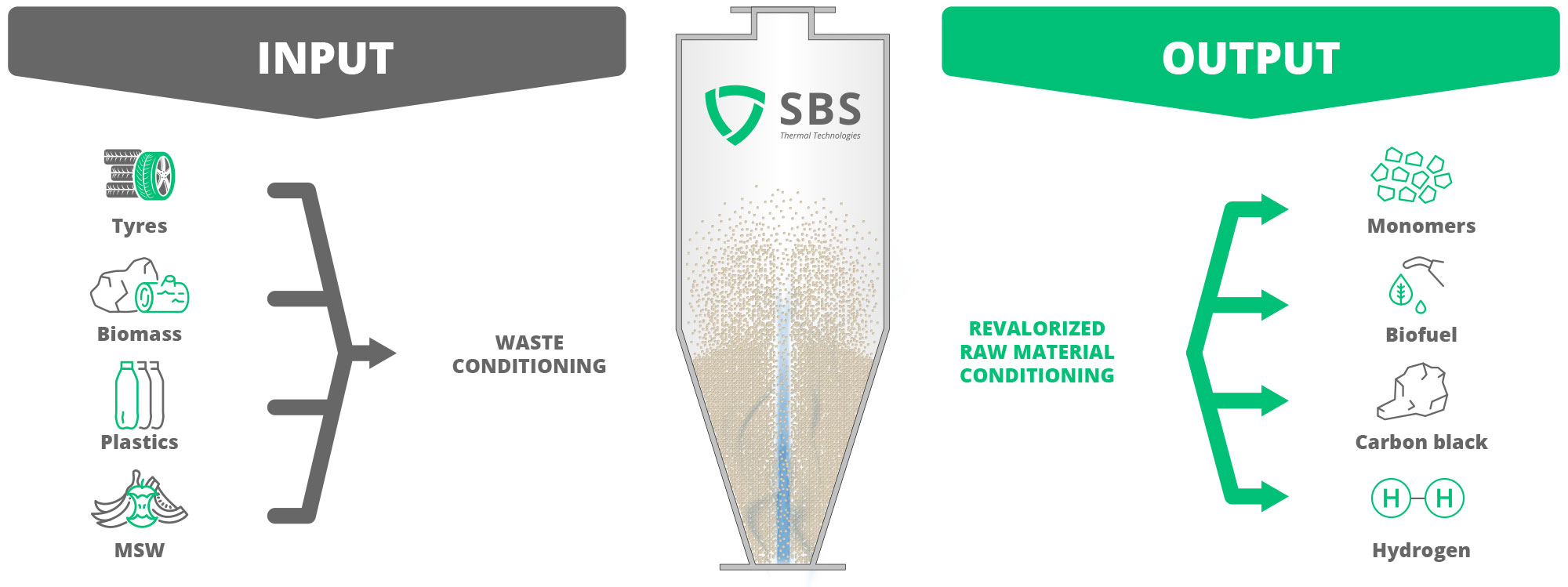
Pyrolisis
Pyrolysis is the heat degradation of a substance in the absence of oxygen. It involves breaking down substances with heat without setting off combustion reactions. This enables waste with organic content to be converted into high value-added products such as monomers, Bio-fuels, carbon black and hydrogen.
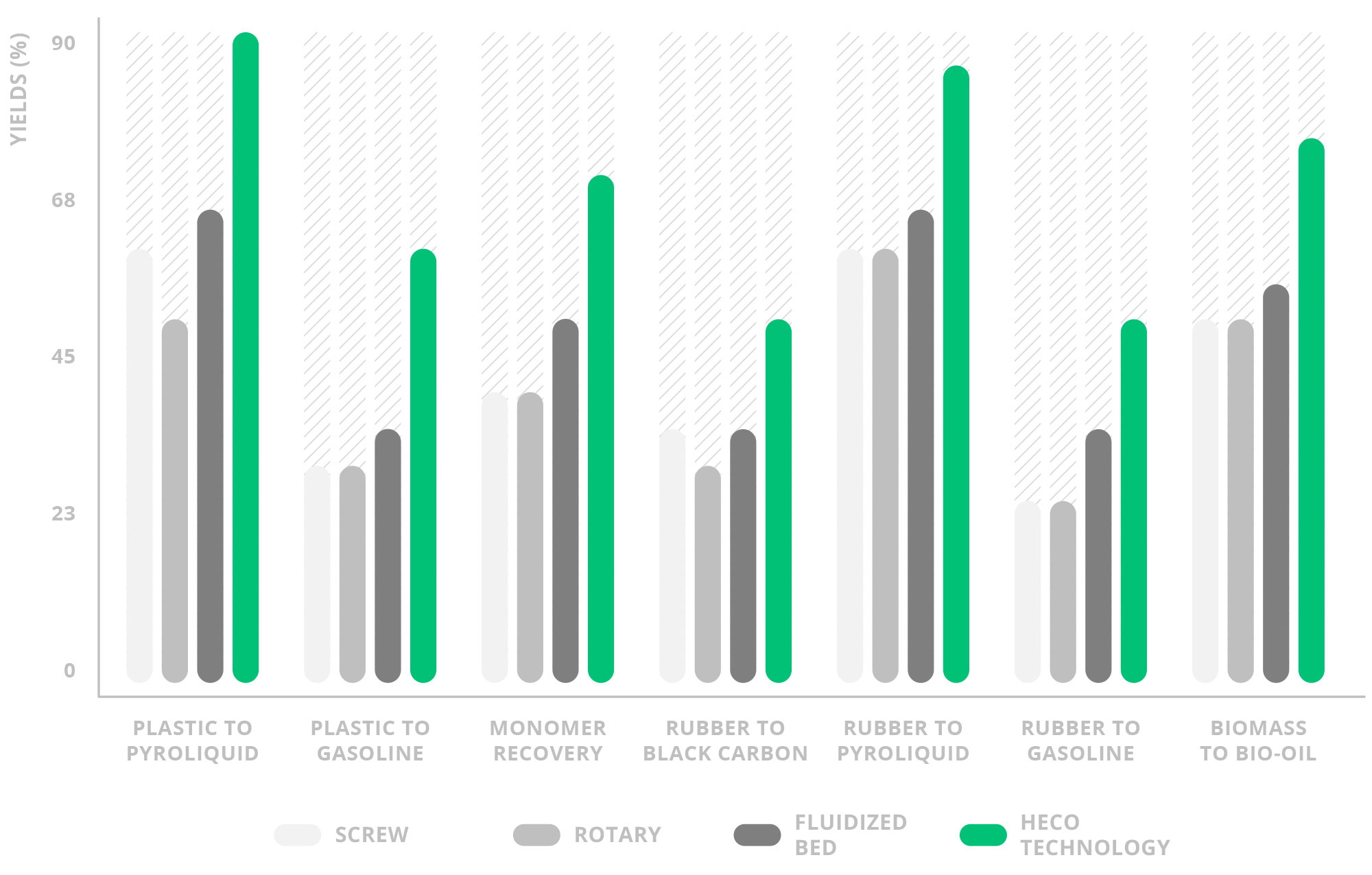
SBS’s HECO technology is more versatile and cheaper than other technologies used in processes of this type. Its characteristic movement is markedly beneficial for the transfer of material and energy, which translates into a drastic reduction in the energy needed in the process and savings in process costs. It also eliminates jams and collapses problems frequently found when dealing with materials such as plastics.
To provide the best possible production conditions, HECO technology can be modulated to suit the material input and the desired product. This results in better performance than other technologies in processes such as the production of monomers, Bio-fuels and carbon black.

Variables that can affect the pyrolysis process
Process temperature
Higher pyrolysis temperatures result in more non-condensable gases, while lower temperatures are conducive to the production of high-quality solids.
Material holding times in the pyrolysis chamber
This influences the degree of heat conversion of the solid received and the steam holding time.
Particle size and physical structure
This affects how fast materials undergo pyrolysis.
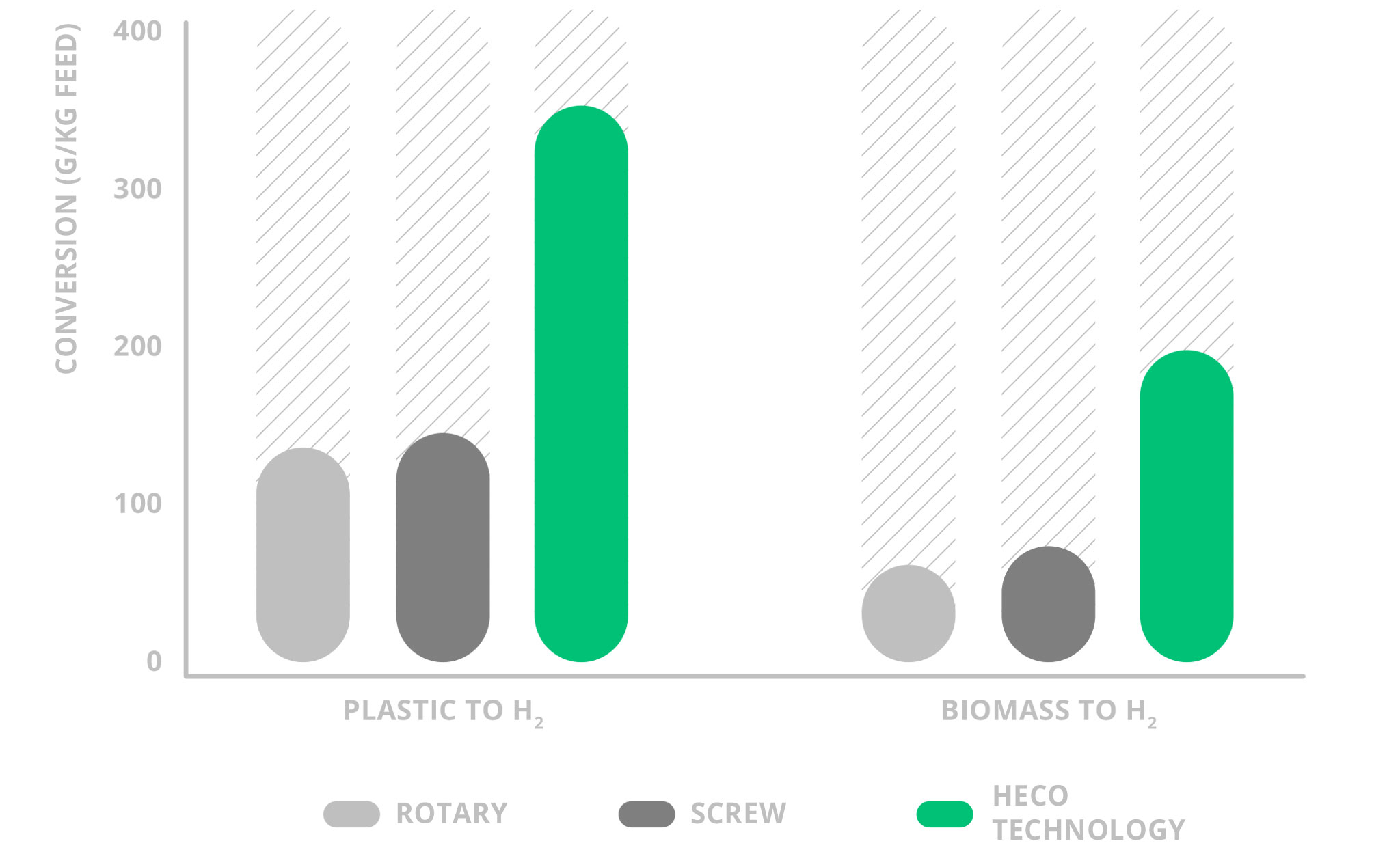
Hydrogen production
SBS has developed a process for obtaining hydrogen via its HECO technology that outperforms other H2 production technologies. This is thanks to the combination of the HECO pyrolysis process with the subsequent reformation stage. The HECO technology produces pyrolysis gases which are suitable for this subsequent stage. Obtaining these gases is key for increasing H2 production. Output may be as much as double that of other technologies in the conversion of plastics and biomass to H2.
Uses of pyrolysis
Our pyrolysis service turns waste into new, valorised raw material.
- Pyrolysis of tyres.
- Pyrolysis of biomass.
- Pyrolysis of plastics.
- Pyrolysis of MSW in hydrogen.

HECO Technology assures higher production ratios than other technologies