Drying
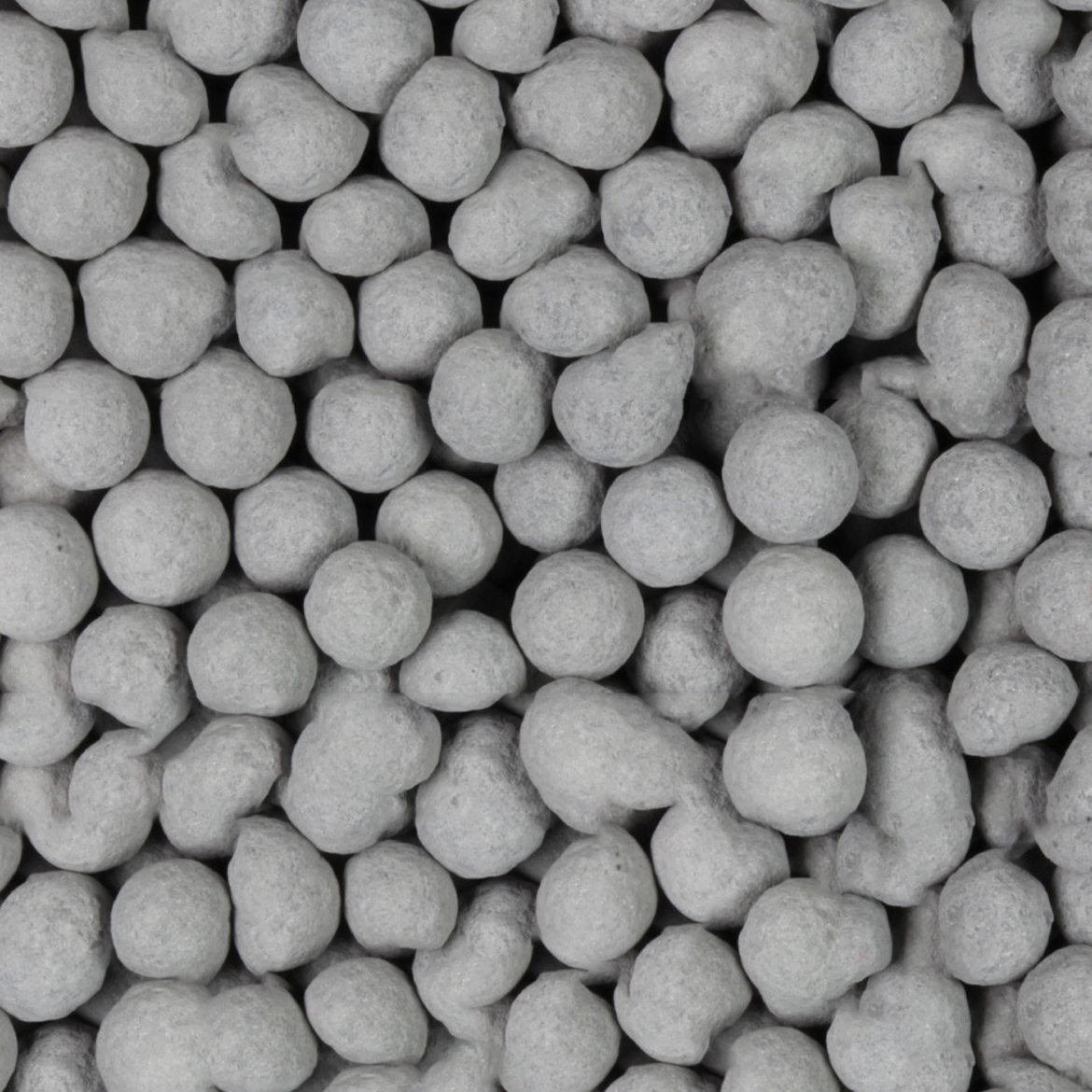
Reactor with bed formed by particles.

Drying
Hot air is fed in through the bottom of the reactor and rises vertically through the bed. This causes the particles to move up and down in a cyclical fashion.

Drying
When they come into contact with the wet material in the updraft there is 90% flash drying. In just a few seconds several cycles are completed and all moisture is evaporated.

Drying
Material is fed in and extracted continuously, resulting in a stream of dry product with a moisture level of around 0%, at an efficiency rate of 95%.

Pyrolysis
Reactor with bed formed by particles.

Pyrolysis
Hot gas is fed in through the bottom of the reactor and rises vertically through the bed. This causes the particles to move up and down in a cyclical fashion.

Pyrolysis
Particles of plastic undergo several processes simultaneously in just a fraction of a second. 1. The particles are melted with residual heat.2. When they come into contact with the moving bed they form a film on the outer surface of the bed particles. This results in a surface area hundreds of times greater for the reaction. 3. When the plastic comes into contact with the hot air stream it is pyrolysed and gives off gases which are then condensed to obtain the end products. The bed particles are then released for the next cycle.

Pyrolysis
Material is fed in and extracted continuously, resulting in a stream of gas with a yield of over 80% in high-value products.
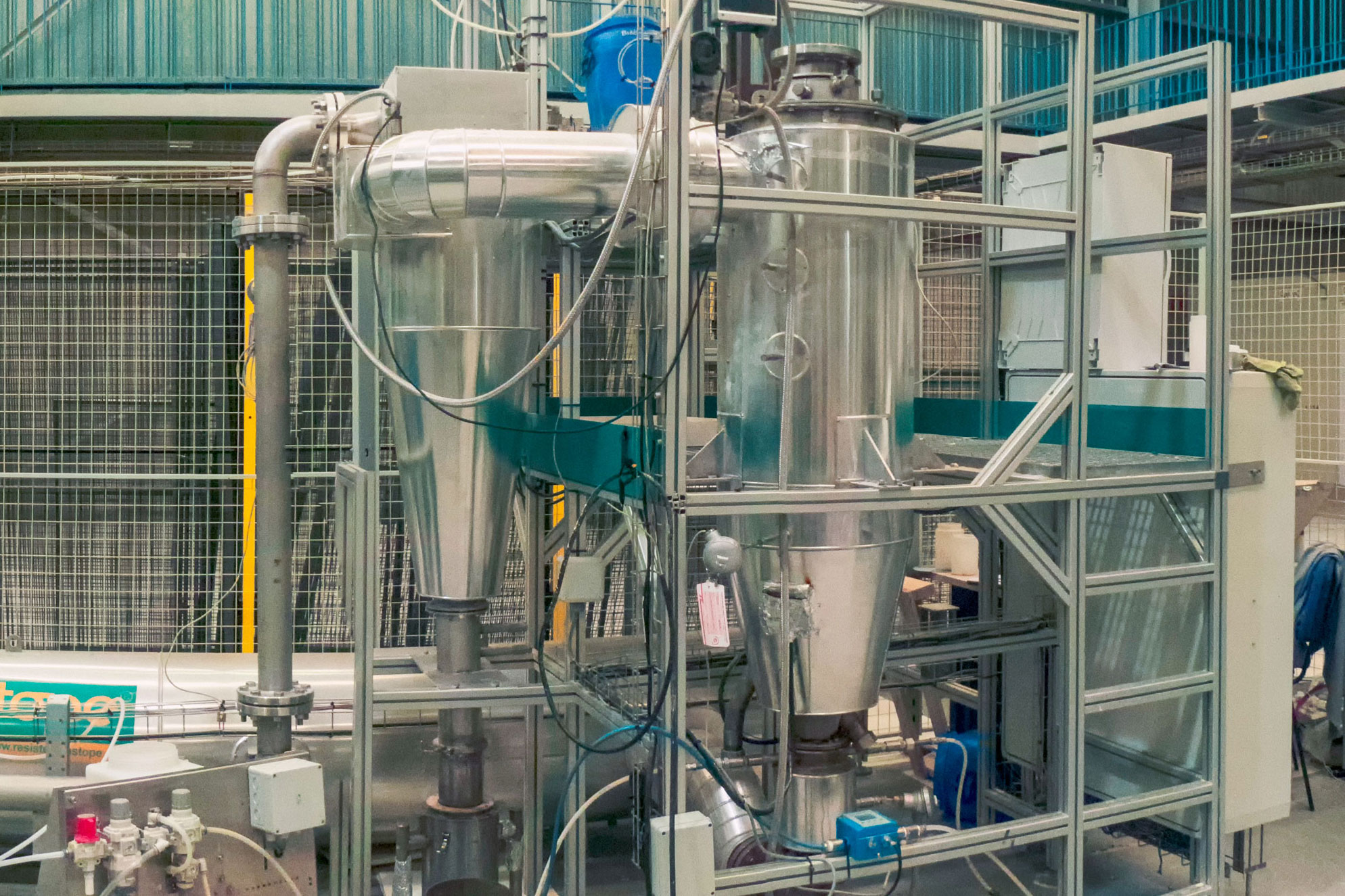
Heat treatment with HECO technology
HECO (High Efficiency Contact) is a patented technology that enables all types of waste to be heat treated, improving process conditions with a view to maximising the amount of desired product (greater effectiveness) with less energy consumption (greater efficiency).
Unlike energy valorisation plants, which focus solely on more polluting, less efficient incineration processes, HECO technology enables more advanced, more sustainable heat treatment processes to be developed, such as pyrolysis, gasification, drying and roasting.

HECO Technology's Benefits
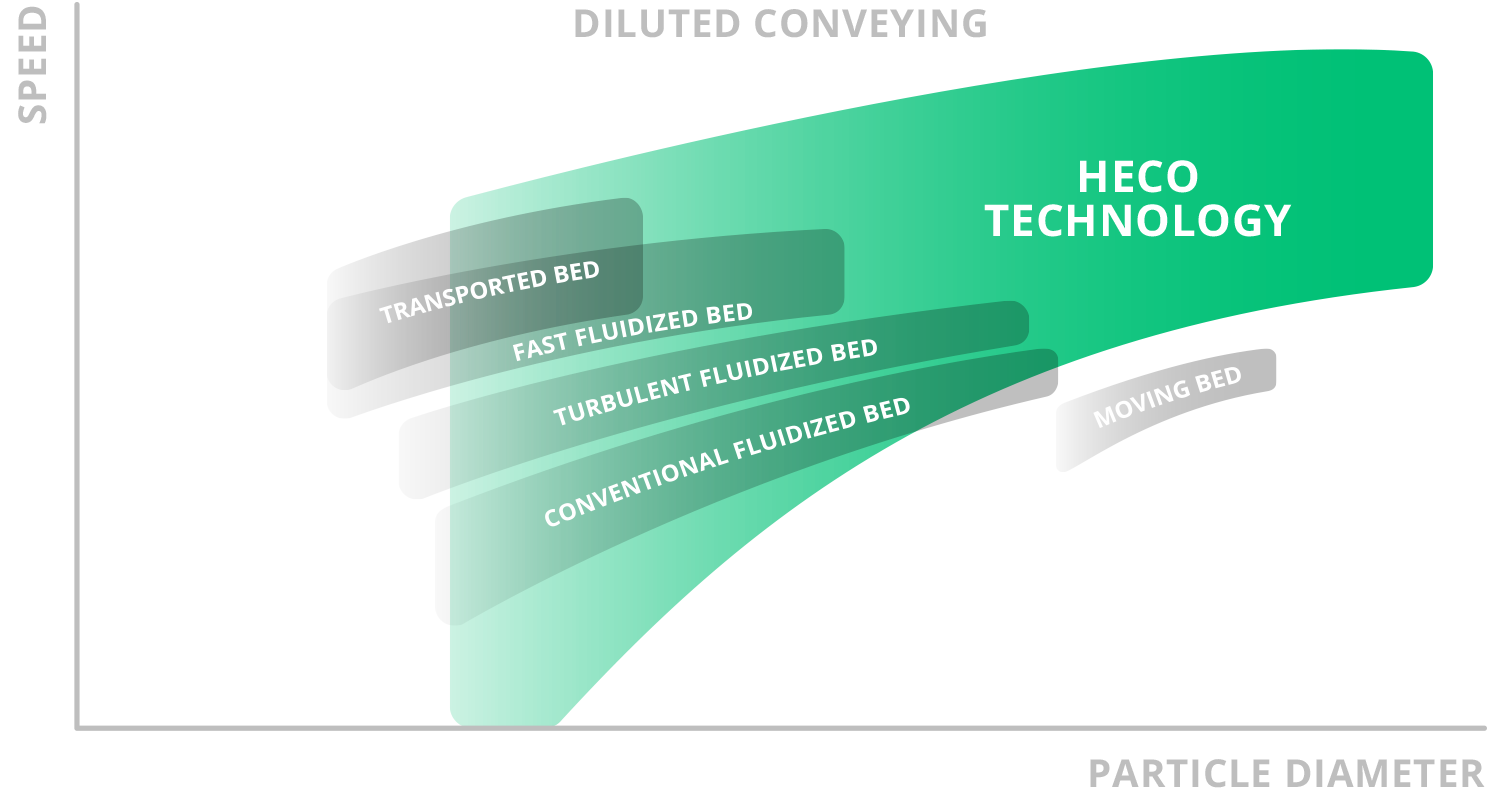
Comparison of HECO with other technologies
The main difference with HECO technology is that it can treat greater numbers of particles of practically any size, and can do so faster than other conventional fluid bed technologies. Application in various processes has shown that it is capable of obtaining the products desired with an energy efficiency of > 95%. It also is able to work with materials of different shapes and properties including sludge, cake, sand and suspended solids.
FAQs
What is the difference between heat valorisation and energy valorisation?
Unlike energy valorisation processes, which are less efficient and more pollutant because they seek only to incinerate waste to obtain energy, heat valorisation seeks to use more advanced, efficient, sustainable heat treatment to give waste a new use.
HECO technology enables heat valorisation processes to be developed that range from drying and pyrolysis to CO2 capture, gasification and roasting. The more than 95% efficiency and the versatility of our technology make it one of the most advanced alternative solutions on the market for valorising waste via heat treatment processes.
What are the financial benefits of heat treating waste in an HECO reactor?
- Savings on local transportation and export costs.
- Efficient recovery of metals.
- Savings in metal separation.
- Revenue from sales of electricity, metals and bottom ash.
- Incentives to use renewables.
- Improvements in coating applications available on the market.
What are the environmental benefits of heat treating waste?
- A far smaller ecological footprint than other disposal methods.
- Generation of sustainable energy.
- Development of biofuels.
Applications
HECO technology is versatile enough to treat many different types of material highly efficiently, and thus has many different applications.









